Adhesión al bundle de prevención de neumonía asociada a la ventilación mecánica
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15649/cuidarte.v10i2.746Palavras-chave:
Unidades de Cuidados Intensivos, Neumonía Asociada al Ventilador, Prestación de Atención de Salud, EnfermeríaResumo
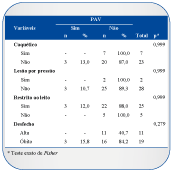
Introducción: Evaluar la adhesión y el cumplimiento de las prácticas que conforman el bundle de prevención de la Neumonía Asociada a la Ventilación Mecánica en una Unidad de Terapia Intensiva de adulto. Materiales y Métodos: Se trata de un estudio descriptivo con enfoque prospectivo, en el que se hizo seguimiento a los pacientes internados en la Unidad de Cuidados Intensivos de una Fundación Pública, bajo ventilación mecánica, en los meses de octubre a noviembre de 2017. La muestra fue no probabilística y correspondió a la observación de los cuidados que conforman el Protocolo de Prevención de Neumonía Asociada a la Ventilación Mecánica. Resultados: Se observaron 30 pacientes bajo ventilación mecánica, para un total de 44 días de observación, durante los que se realizaron 2.002 observaciones. Durante el período de estudio, 3 (50%) de las prácticas se mantuvieron por encima del 80% de la adhesión, lo que demuestra la importancia del monitoreo de los cuidados incluidos en el bundle. Discusión y Conclusiones: Se observó que el cumplimiento de algunas prácticas se encuentra por debajo de lo esperado, lo que demuestra la necesidad de estrategias educativas que promuevan la calidad de todos los cuidados.
Como citar este artigo: Barros FRB. Adesão ao bundle de prevenção de pneumonia associada à ventilação mecânica. Rev Cuid. 2019; 10(2): e746. http://dx.doi.org/10.15649/cuidarte.v10i2.746
Referências
Silva SG, Salles RK, Nascimento ERP, Bertocello KCG, Cavalcanti CDK. Avaliação de um bundle de prevenção da pneumonia associada à ventilação mecânica em unidade de terapia intensiva. Texto & Contexto Enfermagem. 2014; 23(3): 744-50. http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/0104-07072014002550013
Sachetti A, Rech V, Dias AS, Fontana C, Barbosa GDL, Schlichting. Adesão às medidas de um bundle para prevenção de pneumonia associada à ventilação mecânica. Revista Brasileira de Terapia Intensiva. 2014; 26(4): 355-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.5935/0103-507X.20140054
Rodrigues AN, Fragoso LVC, Beserra FM, Ramos IC. Determining impacts and factors in ventilator-associated pneumonia bundle. Rev Bras Enferm. 2016; 69(6): 1045-51. https://doi.org/10.1590/0034-7167-2016-0253
Mota EC, Oliveira SP, Silveira BRM, Silva PLN, Oliveira AC. Incidência da pneumonia associada à ventilação mecânica em unidade de terapia intensiva. Medicina Ribeirão Preto. 2017; 50(1): 39-46. http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/0034-7167-2016-0253
Mishra SB, Azim A, Muzzafar SN. Prevention of ventilator-associated pneumonia and ventilator-associated conditions. Critical Care Medicine. 2015; 43(11): 527-34. https://doi.org/10.1097/CCM.0000000000001184
Kalil AC, Metersky ML, Klompas M, Muscedere J, Sweeney DA, Palmer LB, et al. Management of adults with hospital-acquired and ventilator-associated pneumonia: 2016 clinical practice guidelines by the Infectious Disease Society of America and the American Thoracic Society. Clin Infect Dis. 2016; 63(3): 61-111. https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/ciw504
American Thoracic Society/Infections Diseases Society of America (ATS/IDSA). How-toguide: prevent ventilator associated pneumonia. Cambridge, MA: Institute for Health Care Improvement; 2012.
American Thoracic Society & Infectious Diseases Society of America. Guidelines for the management of adults with hospital-acquired, ventilator-associated, and healthcare-associated pneumonia. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2005; 171(4): 388-416. https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.200405-644ST
Silva HG. Protocolo de Enfermagem na Prevenção da Pneumonia Associada ao Ventilador: Comparação de Efeitos/ Hamanda Garcia da Silva- Niteroi: [Sn], 2010.
Saupe H, Horr L. Auditoria em enfermagem. Revista Ciên Saúde. 1982; 1(1): 23. http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/0034-716719780004000005
Baggio L, Machado AS, Caberlon CF, Junior LAF, Schuster RC. Bundles para prevenção da pneumonia associada à ventilação mecânica. Revista Inspirar Movimento & Saúde. 2016;8(1): 4-9.
Chicayban LM, Terra ELVS, Ribela JS, Barbosa PF. Bundles de prevenção de pneumonia associada à ventilação mecânica: a importância da multidisciplinaridade. Biológicas & Saúde. 2017; 25(7): 25-35. https://doi.org/10.25242/886872520171200
Almeida KMV, Barros OMC, Santos GJC, Valença MP, Cavalcanti ATA, Ferreira KO. Adesão às medidas de prevenção para pneumonia associada à ventilação mecânica. Rev Enferm UFSM. 2015; 5(2):247-256. http://dx.doi.org/10.5902/2179769215411
Khan R, Al-Dorzi HM, Al-Attas K, Ahmed FW, Marini AM, Mundekkadan S et al. The impact of implementing multifaceted interventions on the prevention of ventilator-associated pneumonia. American Journal of Infection Control. 2016; 44(3): 320-6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajic.2015.09.025
Mansano FPN, Belei RA, Vinci LAS, de Melo BLD, Cardoso LTQ, Garcia JCP et al. Impacto de ação educativa na manutenção do decúbito elevado como medida preventiva de pneumonia associada à ventilação mecânica em Unidade de Terapia Intensiva. ABCS Health Sciences. 2017; 42(1): 21-6. http://dx.doi.org/10.7322/abcshs.v42i1.945
Ferreira EG, Kimura A., de Ramos DF, de Albuquerque PL, Antunes MD, de Oliveira DV. Prevalência de pneumonia associada à ventilação mecânica por meio de análise das secreções traqueobrônquicas. Northeast Network Nursing Journal. 2017; 18(1): 140-20. http://dx.doi.org/10.15253/2175-6783.2017000100016
Marra AR, Cal RGR, Silva CV, Caserta RA, Paes AT, Moura DF et al. Successful prevention of ventilator-associated pneumonia in an intensive care setting. American Journal of Infection Control. 2009; 37(8): 619-25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajic.2009.03.009
Leal GA, Ribeiro JB, dos Santos JJ, Cavalcante AB. Cuidados de enfermagem para prevenção da pneumonia associada à ventilação mecânica em unidades de terapia intensiva: uma revisão literária. Ciências Biológicas e de Saúde Unit. 2017;4(1): 95-108.
Publicado
Como Citar
Downloads
Edição
Seção
Licença
A Revista Cuidarte é um acesso aberto publicação científica, distribuído sob os termos da Creative Commons Atribuição (CC BY-NC 4.0), que permite uso irrestrito, distribuição e reprodução em qualquer meio, desde que o autor ea fonte original eles estão devidamente citada.
Qualquer outro uso, como reprodução, transformação, comunicação pública ou de distribuição, com fins lucrativos, requer a aprovação prévia da Universidade de Santander UDES.
Os nomes e endereços informados na Revista Cuidarte serão usados exclusivamente para os serviços prestados por esta publicação, não estará disponível para qualquer outro propósito ou outra pessoa.
Os artigos publicados na Revista Cuidarte representam os critérios da responsabilidade dos autores e não representam necessariamente a posição oficial da Universidade de Santander UDES.



